Ever come across the nutrition myth that ‘desi ghee will make you fat’?
Chances are, it’s been a recurring theme in your social media feed and group chats.
The digital age has made it effortless for unqualified sources to share supposed ‘food cures’ for various ailments.
Today, we’re delving into the myriad of nutrition myths circulating online, separating fact from fiction.
Let’s debunk and discard these misconceptions for a healthier, well-informed lifestyle.
1. No Eating After 7 p.m.

Late-night snacking isn’t inherently tied to weight gain; it’s about the reasons behind it. Whether due to habit, boredom, or cravings, eating in the evening isn’t problematic solely because of the clock. Understanding why you eat matters more than when.
2. Rethinking Weight Loss: Beyond “Calories in, Calories out”

Another nutrition myth is that a calorie deficit is crucial for weight loss, but it’s not the sole determinant. Factors like hormonal imbalances, health conditions, and genetics play a role. Emphasizing sustainability and diet quality is equally vital, as focusing solely on calorie intake overlooks nutrient value.
3. The Low-Fat Trap: Are Fat-Free Products Truly Healthier?

Don’t fall for the low-fat or fat-free illusion. Many such products compensate for reduced fat with added sugar or sodium, hindering their nutritional value. Fat aids in satiety, making you feel fuller longer. Opting for fat-free products in an attempt to cut calories may backfire, leading to post-snacking cravings.
4. Desi Ghee and Weight Gain

Contrary to popular nutrition myths, desi ghee doesn’t make you gain weight. Packed with healthy fats, short-chain fatty acids, and vital vitamins, desi ghee supports digestion, heart health, and more. Enjoying 2–4 tablespoons daily benefits everyone, regardless of fitness goals.
5. Peanut Butter’s Nutritional Reality: Not Extra Fatty

Cutting this nutrition myth of peanut butter being considered extra fatty, it is a nutritious choice, with almost 50% healthy fats, including heart-friendly oleic acid and essential Omega-6 fatty acids. These components support heart health and insulin sensitivity.
6. Health Isn’t Defined by Skinny Size

Health isn’t synonymous with being skinny. While obesity is linked to various health conditions, prioritizing a nutritious diet and an active lifestyle matters more than achieving a particular body size, debunking another nutrition myth. Improving body weight and fat percentage through healthy behaviours is key.
7. Gluten-Free for Weight Loss? Not necessarily

The idea that cutting gluten aids weight loss isn’t universally true. Unless you have celiac disease or gluten intolerance, there’s no need to avoid gluten. Weight loss comes from a calorie deficit, not a gluten-free diet. Make sure to have a sensible approach for those without gluten-related health issues.
8. Breakfast’s Role: “Most Important Meal” Myth

Contrary to the belief that breakfast is indispensable, research suggests otherwise for most adults, debunking this nutrition myth. Skipping breakfast, as seen in intermittent fasting, can have health benefits like improved blood sugar control. However, individual preferences matter, and health benefits are associated with both eating and skipping breakfast.
9. Meal Frequency: Separating Fact from Fiction

The idea of eating small, frequent meals for metabolic benefits is widespread. However, for healthy individuals, meal frequency is less critical than meeting energy needs. Certain medical conditions may necessitate more frequent meals, but overall, a regular meal pattern is emphasized for optimal health, dispelling the need for constant snacking.
10. Smoothies and Juices: Not All Are Healthy
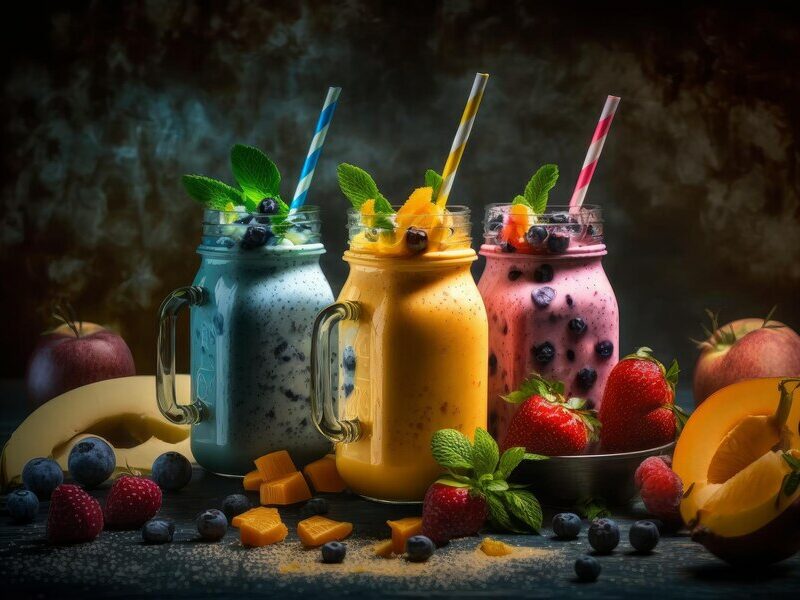

While nutrient-packed smoothies and juices made from non-starchy vegetables can be nutritious, beware of store-bought versions. Many are loaded with sugar and calories, contributing to weight gain and health issues like tooth decay. Differentiating between wholesome and sugar-laden options is essential for making healthier choices.
Conclusion
Popular nutrition myths can sometimes be misleading. Timing matters less than the reasons behind our food choices, and the assumption that all fat-free products are healthier is a misconception. Health isn’t confined to a specific body size, emphasizing the importance of balanced lifestyles over a pursuit of thinness. Navigating these myths requires a thoughtful consideration of individual habits and making informed choices that prioritize overall well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the golden rule for nutrition?
The 80/20 Rule: Each meal and snack is an opportunity to replenish your body optimally. Choose the foods that are best for you 80% of the time and incorporate some of those foods that may not be the best, but are your favorites, 20% of the time! Life is about balance!
What is the biggest nutrition myth?
Fresh fruits and vegetables are always healthier than canned, frozen or dried varieties. Despite the enduring belief that “fresh is best,” research has found that frozen, canned and dried fruits and vegetables can be just as nutritious as their fresh counterparts.
Did you know food nutrition facts?
An avocado has more than twice as much potassium as a banana. Broccoli contains twice the vitamin C of an orange and almost as much calcium as whole milk, and the calcium is better absorbed!